WHAT IS A FRACTAL ?
WHAT IS A FRACTAL ?
A fractal is a never-ending pattern. Fractals are infinitely complex patterns that are self-similar across different scales. They are created by repeating a simple process over and over in an ongoing feedback loop. Driven by recursion, fractals are images of dynamic systems – the pictures of Chaos. Geometrically, they exist in between our familiar dimensions. Fractal patterns are extremely familiar, since nature is full of fractals. For instance: trees, rivers, coastlines, mountains, clouds, seashells, hurricanes, etc. Abstract fractals – such as the Mandelbrot Set – can be generated by a computer calculating a simple equation over and over.
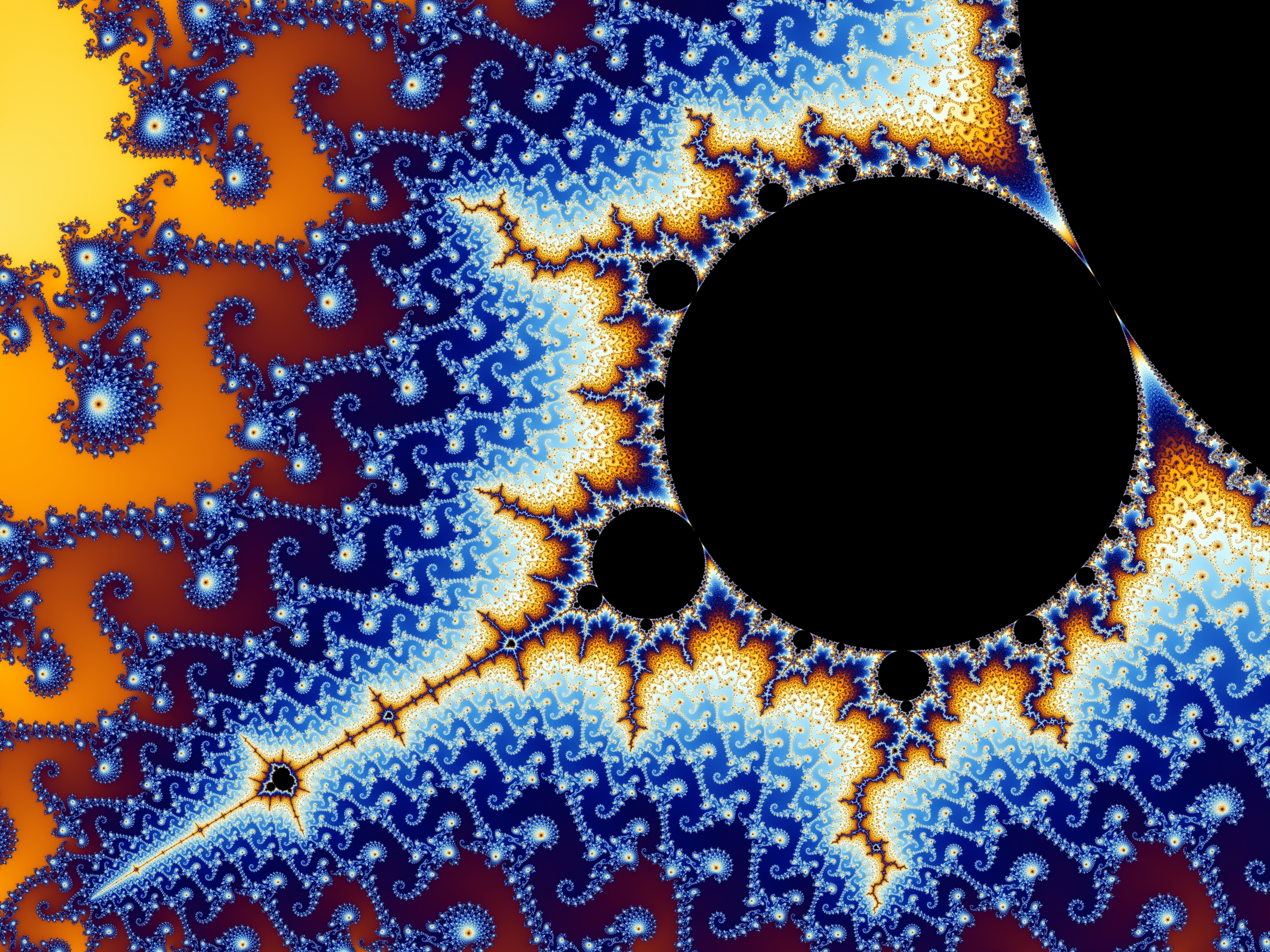 |
| Mandelbrot Set |
In mathematics a fractal is an abstract object used to describe and simulate naturally occurring objects. Artificially created fractals commonly exhibit similar patterns at increasingly small scales. It is also known as expanding symmetry or evolving symmetry. If the replication is exactly the same at every scale, it is called a self-similar pattern. An example of this is the Menger sponge. Fractals can also be nearly the same at different levels. This latter pattern is illustrated in small magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. Fractals also include the idea of a detailed pattern that repeats itself.
Fractals are different from other geometric figures because of the way in which they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the dimension of the space the polygon resides in). Likewise, if the radius of a sphere is doubled, its volume scales by eight, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old radius) to the power of three (the dimension that the sphere resides in). But if a fractal's one-dimensional lengths are all doubled, the spatial content of the fractal scales by a power that is not necessarily an integer. This power is called the fractal dimension of the fractal, and it usually exceeds the fractal's topological dimension.
As mathematical equations, fractals are usually nowhere differentiable. An infinite fractal curve can be conceived of as winding through space differently from an ordinary line, still being a 1-dimensional line yet having a fractal dimension indicating it also resembles a surface.
I am interested to study about fractals....pls upload more articles abt fractal geometry...
ReplyDeleteWe are glad to hear from you.. much more interesting facts regarding fractals will be uploaded soon..
ReplyDelete